Allergy testing
Allergy testing is performed to identify substances that cause allergic reactions in individuals.
There are several methods for allergy testing, and the choice of method depends on the specific circumstances and the type of allergies being investigated. Here are some common methods used for allergy testing. Click on allergy test to learn more.
Types Of Allergy Testing
1Intradermal Test:
Similar to the skin prick test, this involves injecting a small amount of allergen under the skin with a thin needle. This test is more sensitive than the skin prick test and is often used when the skin test results are inconclusive.
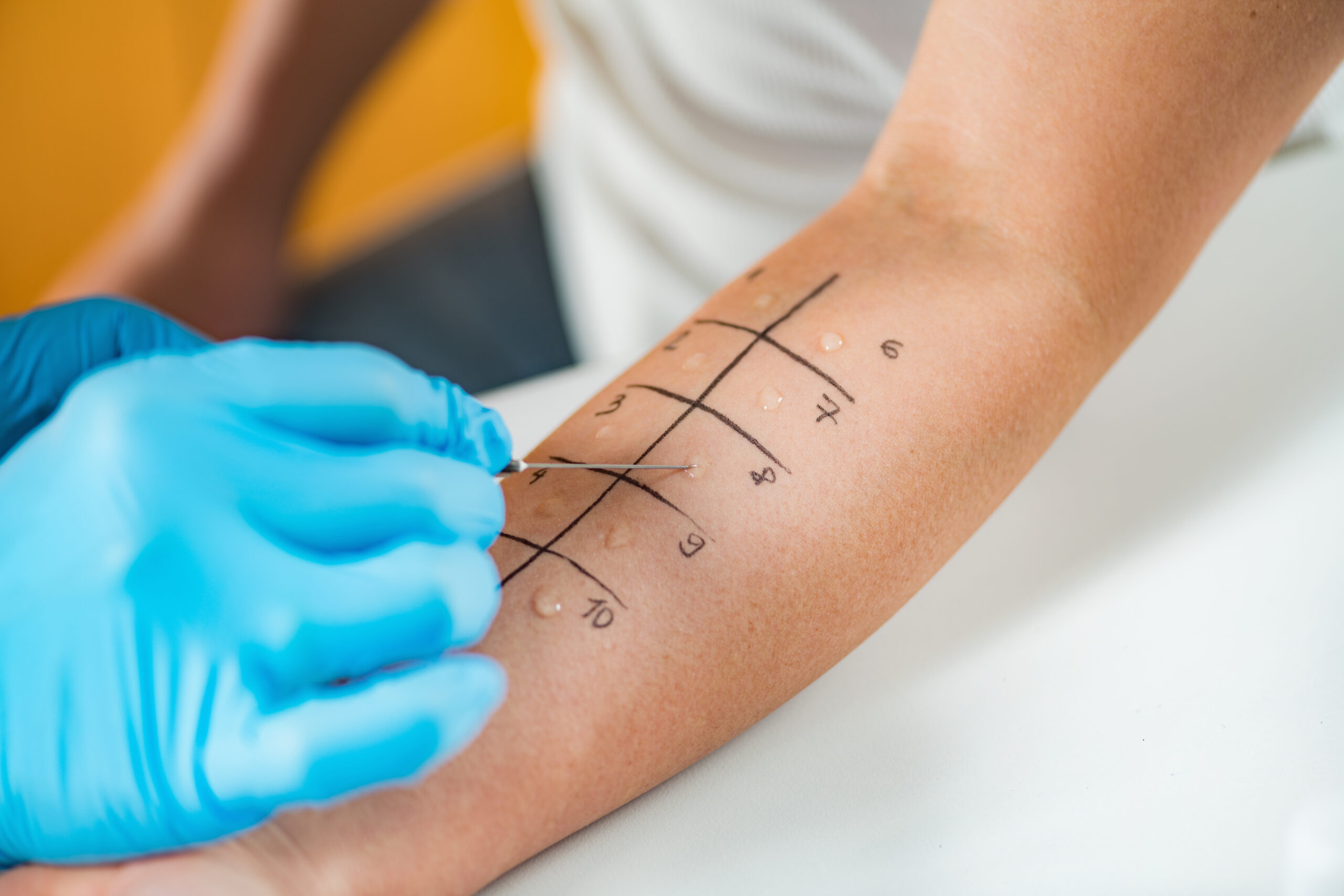
2Skin Prick Test (SPT):
This is one of the most common methods for allergy testing. In an SPT, a small amount of allergen extract is applied to the skin, usually on the forearm or back. The skin is then pricked with a tiny needle, allowing the allergen to enter the skin. If a person is allergic to the substance, a small raised bump called a wheal will develop at the test site.
3Blood Test (Serology):
Blood tests, such as the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or radioallergosorbent test (RAST), measure the amount of specific antibodies (IgE) produced in response to particular allergens. Blood tests are useful when skin testing is not possible or may be less accurate, such as in the presence of certain skin conditions or if the patient is taking medications that interfere with skin test results.
4Elimination Diet:
In cases where food allergies are suspected, an elimination diet may be recommended. This involves removing suspected allergens from the diet for a specific period and then reintroducing them one at a time to identify the culprit.
It's important to note that allergy testing should be conducted and interpreted by qualified healthcare professionals, such as allergists or immunologists. The choice of testing method depends on factors like the patient's medical history, the suspected allergens, and the type of allergic reactions observed. Additionally, not all positive test results indicate clinical allergy, so proper clinical correlation is crucial.

